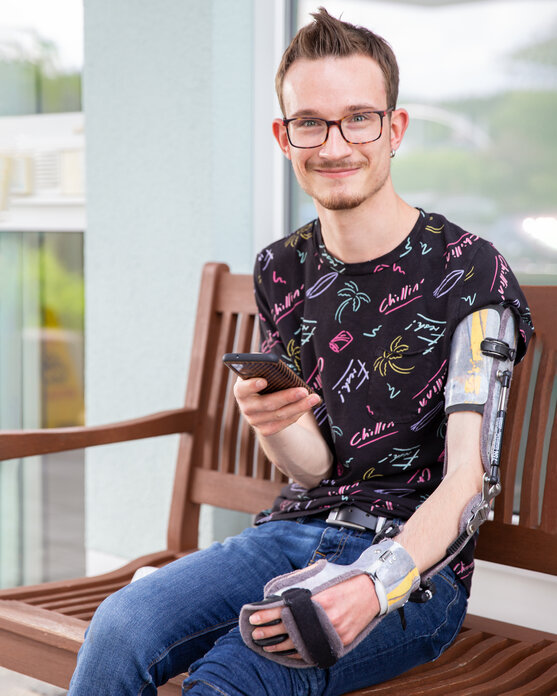
An orthosis compensates for physical deficits, supports joints and protects them from relapse and misalignment.
Thanks to SimBrace® we can simulate your orthosis before we produce it.
Make an appointment over the phone or send us a message!

Aids for protecting and supporting
Orthoses for finger,
hand, and arm
A properly fitted orthosis compensates for deficits, supports joints, and slows down or prevents the progression of joint deformities. Orthoses for the upper extremities are primarily used to improve hand and arm function. Successful orthotic treatment achieves gentle correction and stabilization of the affected hand, all the while maintaining the highest level of function possible.
Depending on the deformity, orthoses can be used short-term or permanently. In order to limit unwanted movement or correct skeletal deformities, orthoses, in contrast to flexible bandages, are usually made of stronger materials like plastic. Orthoses can also offer support post-surgery by providing targeted stabilization and controlling range of motion of the joints. This facilitates the functional development of the hand or arm.

A key prerequisite for a successful orthotic treatment is consistent use of the device. This can only be achieved if you fully accept your finger, hand, or arm orthosis and wear it consistently in everyday life. To make them as comfortable as possible for you to wear, we produce orthoses that are highly functional and visually appealing.
We make sure to use light materials, so that the weight of the device does not cause any additional impairment. We also offer a wide range of different colors and designs for all orthoses so you can customize them to your liking.

Orthoses are generally only prescribed after an in-depth examination by a physician. Ideally, the choice of the appropriate device should always be made in collaboration with a physician, physiotherapist and orthopedic technician.
We are very keen to ensure this interdisciplinary cooperation. Teamwork plays a crucial role in the care of children with orthopedic aids. All participants are in the same boat. After all, optimum treatment results can only be achieved if doctors, orthopedic technicians, therapists, patients and parents all work together.
PRINTORTHESE®
Hand orthosis from the
3D printer
3D printing is increasingly being used in technical orthopedics. Using this method, orthoses can be digitally designed first and then constructed in layers.
Compared to conventional hand orthoses, patients treated with PRINTORTHESE® use the affected hand more frequently during bi-manual activities and report increased wearing comfort.


Aid for children with arm plexus palsy
Concept 4D orthosis (Pohlig/Bahm)
We have developed a dynamic corrective positioning orthosis for children with a condition following obstetrical brachial plexus palsy (OBPP). It consists of individual modules that are used depending on the required mode of action. Due to its special design, the Concept 4D orthosis can act in four dimensions simultaneously.

The POHLIG system
To ensure that a finger orthosis, hand orthosis, or arm orthosis fulfills its function, the orthopedic technician adapts it individually to the child's body. This is the only way to ensure the best possible state-of-the-art care.
Thinking of the body as different segments is very effecitve when planning orthotic treatment. Only once the individual levels of the body have been discussed on an interdisciplinary basis can the therapeutic goal and design specifications of the orthosis be identified and defined. In practice, this means that we proceed from top to bottom (e.g. from shoulder to arm to hand) and define the corrective measures step by step.
With the POHLIG system, a system in which the individual orthosis elements are put on separately, we can accommodate even the most complex misalignments. The POHLIG system offers the option for isolated stretching, bending, and rotation of the extremities, and thus enables a targeted therapy.
Static or dynamic?
Static orthoses are intended to bring affected joints into a corrected position. Dynamic orthoses, on the other hand, apply force to correct malpositions (such as tendon shortening) by such means as spring hinges or gas springs.
Different designs can be selected depending on the clinical picture and characteristics (e.g. ICP, AMC, plexus paralysis, radial aplasia, etc.):
- Individual finger sockets for correcting each finger in the orientation and joint position
- Dynamic joints for flexion, extension, pronation or supination
- Different closure systems
- Adapters that allow putting on individual components of the orthosis
Static and dynamic orthoses are often worn at night. At night, the affected limb can be fixed or corrected over a long period of time. More functional orthoses are usually made for daytime use.


Suit against spastics
The Exopulse Mollii Suit activates muscles
The Mollii Suit is designed for patients suffering from spastic paralysis (i.e. increased muscle tension) and other neurological movement disorders.
By releasing spastic, cramped or painful muscles with gentle electrical pulses, the suit can reduce pain and reactivate important muscles. Many sufferers show a more fluid gait pattern thanks to the Mollii Suit. They have less pain and can be more active in their daily lives.
Flexible aids for the hand and arm
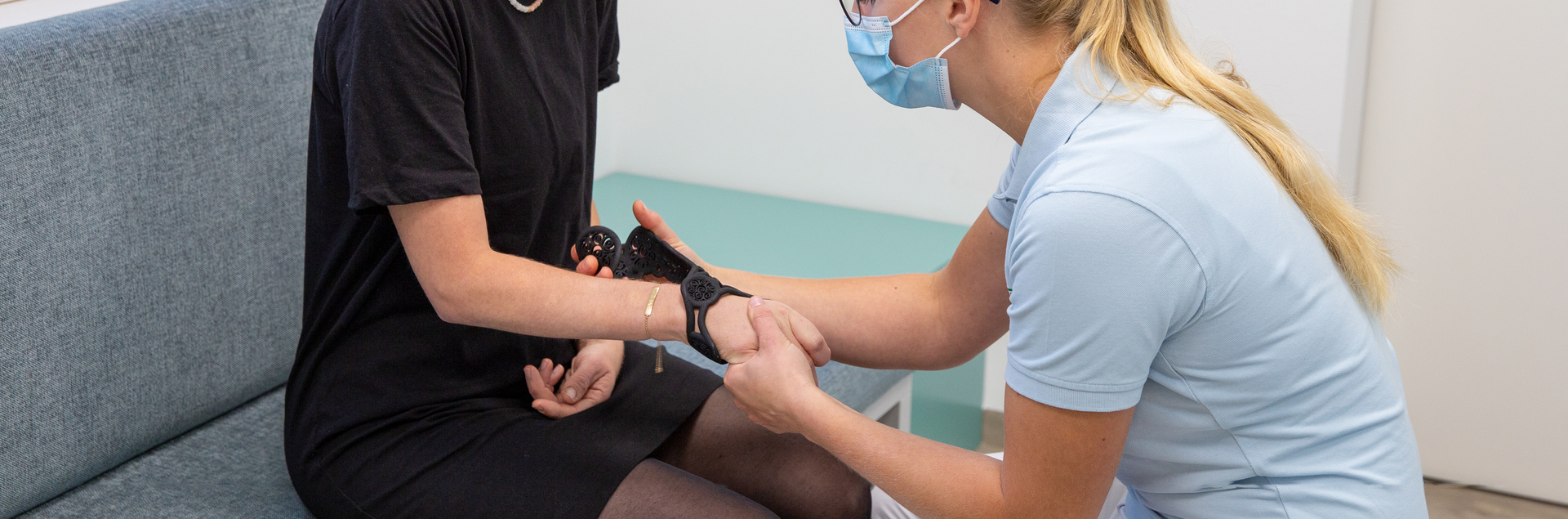
Silicone orthoses
Silicone is a soft, flexible material and therefore very comfortable to wear. Thanks to their elasticity, silicone orthoses can assist the important movements and muscle functions of the hand. At the same time, the material is so stable that it provides optimum support and protection. Silicone adapts to the patient’s hand exceptionally well and is also water-resistant.
Silicone can be worn directly on the skin, as the material is biocompatible and is hypoallergenic. Thanks to the smooth and resilient properties, excellent solutions can be produced even in the most difficult cases.


Let yourself be inspired! We accompany many interesting patients during their Pohlig appointment and give you personal insights.

For those who want to delve even deeper into the matter, we have a suitable video for almost every supply area.

Take a look behind the scenes at Pohlig and find out about diagnoses and our innovative aid solutions!
Silicone hand orthoses
Dressing and cleaning instructions
A silicone orthosis should be cleaned at least once a day:
- open the Velcro fasteners of the orthosis
- hold the silicone orthosis under the tap
- now add a little soap to a conventional hand brush. You can use either normal hand soap, dish soap or shower gel.
- use the brush to lather the orthosis thoroughly. It is best to use a toothbrush for the smaller openings.
- then rinse the orthosis well with water. Soap residue can cause skin irritation.
- dry the orthosis thoroughly with a towel.
In this video, you will learn how to put on your silicone orthosis correctly:
- open the Velcro fasteners of the orthosis.
- lubricate the inside of the orthosis with a little petroleum jelly (i.e. Vaseline)
- apply Vaseline to the lower flap of the silicone orthosis so that the two flaps slide better over each other.
- close the orthosis by placing the upper flap (with the Velcro fasteners) over the lower flap. Be careful not to pinch your skin and make sure that the flaps close flush!
- now close the Velcro fasteners. With three Velcro fasteners, it’s best to start with the middle.

How to put on a silicone orthosis
There are a few things to keep in mind when putting on a silicone orthosis. In the following instructions, we will show you step by step how to put on the silicone orthosis correctly.